Die design and production of parts
8-STAGE DIE DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
Our standardised process for the development of clients’ products is a guarantee of quality in the manufacture of the end product.
Thanks to this process, we can check, systematically, the status of the development and the compliance with the customer’s requirements
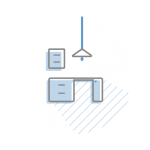
1. CUSTOMER DRAWING
2. SIMULATION AND STRIP DEVELOPMENT
3. DIE DESIGN
4. DIE MANUFACTURE
5. DIE TRYOUT
6. PART DIMENSIONAL INSPECTION (GOM)
7. CP CPK
8. PRODUCTION
1. CUSTOMER DRAWING
The first step is to receive the final drawing. Typically, the client sent the same drawing at an earlier stage in order to receive a quotation for die and production.
At this stage, we need the final data set to begin with the die development.
In the quotation phase, all potential criticalities in die and product development have already been considered.
In special cases, we provide a simulation (to highlight any modifications to be made to the part) or manufacture soft tools in order to produce functional prototypes of the parts.
This last option meets also the client’s need to carry out test assemblies and field testing of the part before starting the production of the definitive dies.
Flli Poli is equipped with 3D laser cutting equipment and can therefore provide the customer with this advantageous interim solution to avoid possible costly future modifications and speed up the delivery of first samples.
2. SIMULATION AND STRIP DEVELOPMENT
For particularly critical products, the simulation of the stamping is sometimes necessary to verify the consistency between the part shape and the material used.
Thanks to the simulation, we can ask for possible geometry modifications to avoid any forming problems related to the material used.
Once the final data set is available, we can start the development of the final strip. This stage is also known as method.
Normally this phase coincides with the validation of the last strip developed (the one made with the first data in order to prepare the offer for the production of the stamped parts).
Any production criticalities are addressed at this time.
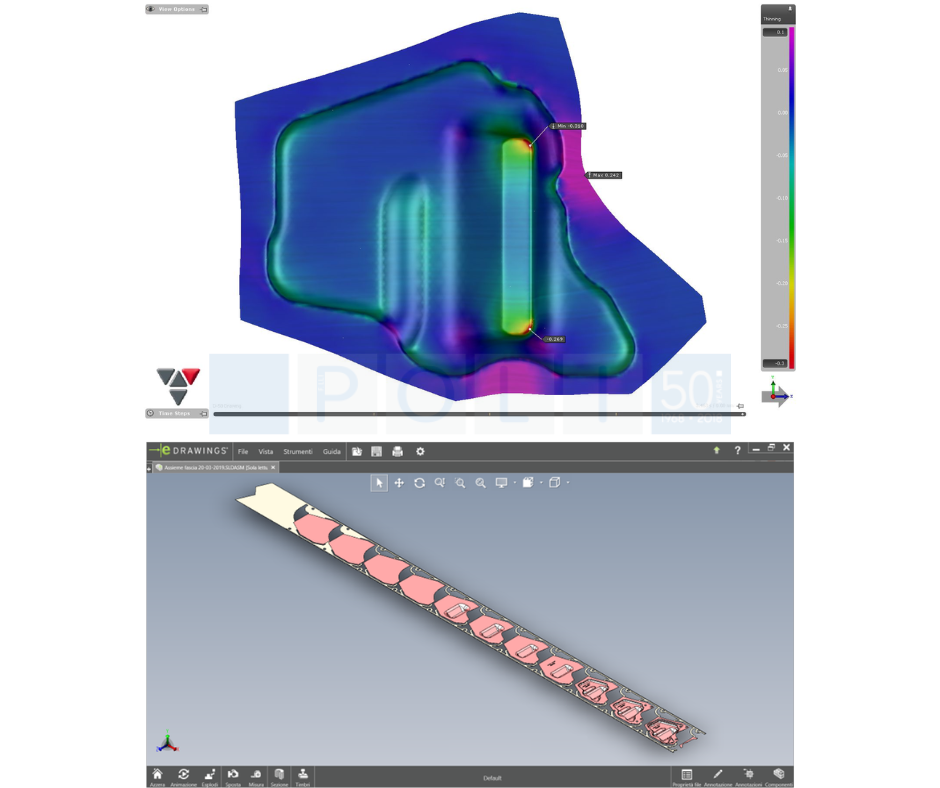
3. DIE DESIGN
The development of the die project is the core of our business and is based on the experience F.lli Poli gained in over 50 years of activity.
At this stage, possible criticalities are identified and our objective is to design the dies so that optimizations are possible with low marginal costs.
The design of a deep-drawing die is completely different from the design of a progressive die.
When it comes to deep-drawing, the main issue is to enable intervening easily in the production process to avoid breakages of the part at the major stretching points as the characteristics of the material (of metal sheet available on the market) change.
When it comes to designing a progressive die, it is crucial to consider any potential stamping criticalities due to raw materials with different characteristics (thickness, springback or elastic modulus) which require a later reworking of the parts. With this in mind, idle steps on the die are provided to handle such potential criticalities.
With progressive dies the designer must be able to minimise the strip width (with important savings in raw material during production) and limit the size of the die so that it can be installed on smaller presses (thus saving on machine cost during production).
Accurate design can lead to savings of up to 30% on the value of the final cost of the part (compared to a superficially executed design).
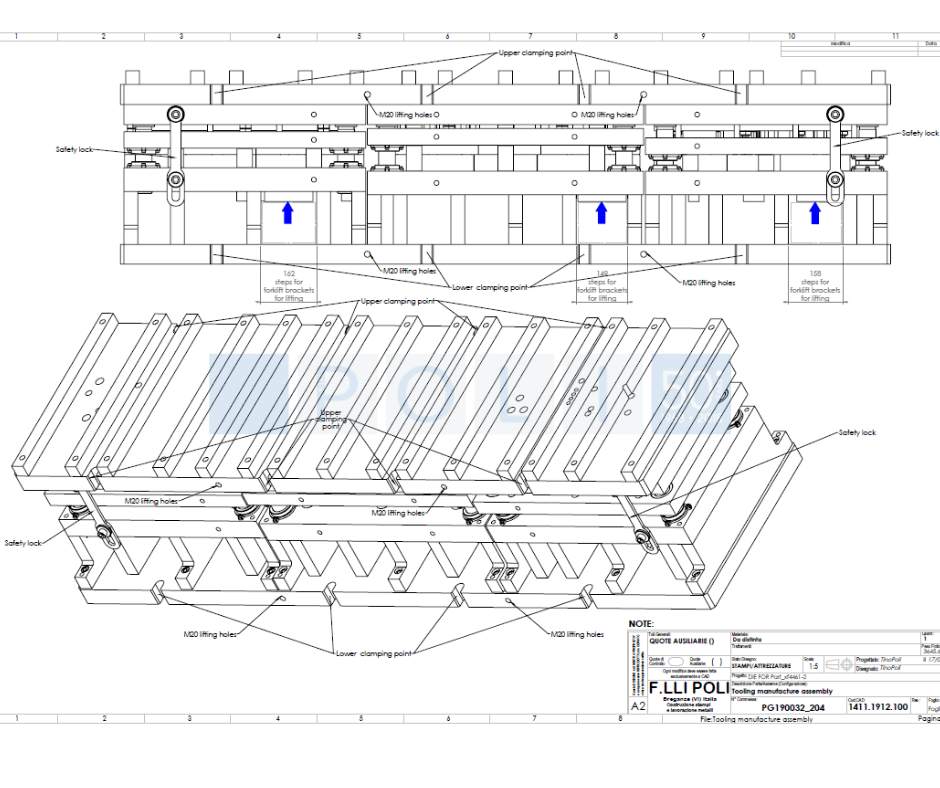
4. DIE MANUFACTURE
F.lli Poli starts to develop the dies using in-house technologies. The course of the project is monitored on a weekly basis by checking the Gantt-diagram that defines time and cost targets.
Monitoring the course of the project is crucial to achieve the delivery target agreed with the customer.
Only through continuous monitoring we can develop the die according to the delivery terms agreed with the client.

5. DIE TRYOUT
Once the deep-drawing die or progressive die has been completed, and particularly when it is first closed, an initial test is carried out to check whether the die itself behaves in a manner consistent with that assumed during the design phase.
Normally the part stamped in this first test is not completely in tolerance.
At this time, initial feedback on the product is gathered so that the designers can introduce corrective actions on the die to eventually obtain the part as designed.
At this stage, the experience of the designers is crucial. The deep-drawing die or progressive die could operate differently from what assumed at the design stage. At this point, the real situation is analysed and tool fine-tuning is carried out keeping the project’s requirements into consideration.
If the client needs prototype parts to verify their functioning in a short time, F.lli Poli provides 3D Laser Cutting technology to make the first components before the die is ready.
In fact, 3D Laser Cutting allows the finished part to be obtained before the entire trimming area in the progressive die, or the trimming die in the case of deep drawing dies, has been completed.
Functional prototypes can thus be made in a very short time. The client can validate the process or introduce modifications with a timeframe that allows any corrective actions on the final product, before the die is ready, thus minimising any modification costs.
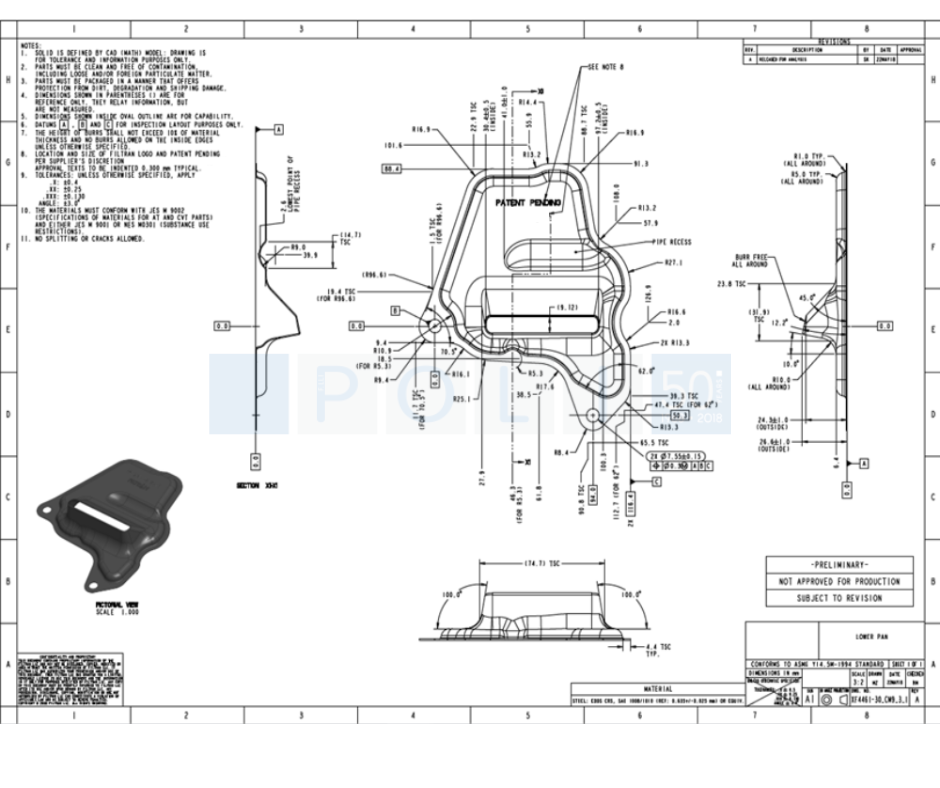
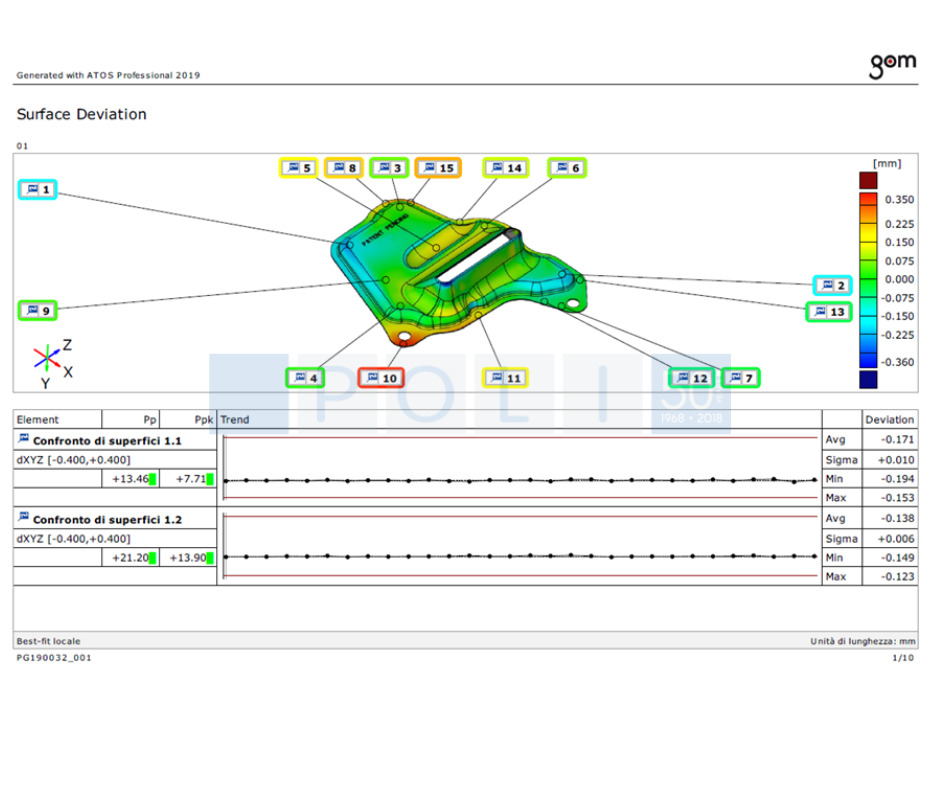
6. PART DIMENSIONAL INSPECTION (GOM)
A variety of methods can be used for the dimensional inspection of the part.
F.lli Poli has decided to invest in an excellent technology for the contactless measurement of components. This enables the complete part to be measured and not only some areas.
The system is based on a state-of-the-art scanner capable of recreating the surface of the scanned object in a digital geometric file in order to compare it with the original geometry of the part in 3D.
This system has several advantages:
● it allows the entire surface to be checked by providing clear indications of any deviations from the nominal dimensions (both in + or -);
● by scanning the component both externally and internally, the thickness of the part can be, point by point measured, to verify any possible points or areas where the thickness is below the minimum value necessary to guarantee the reliability of the part.
7. CP CPK
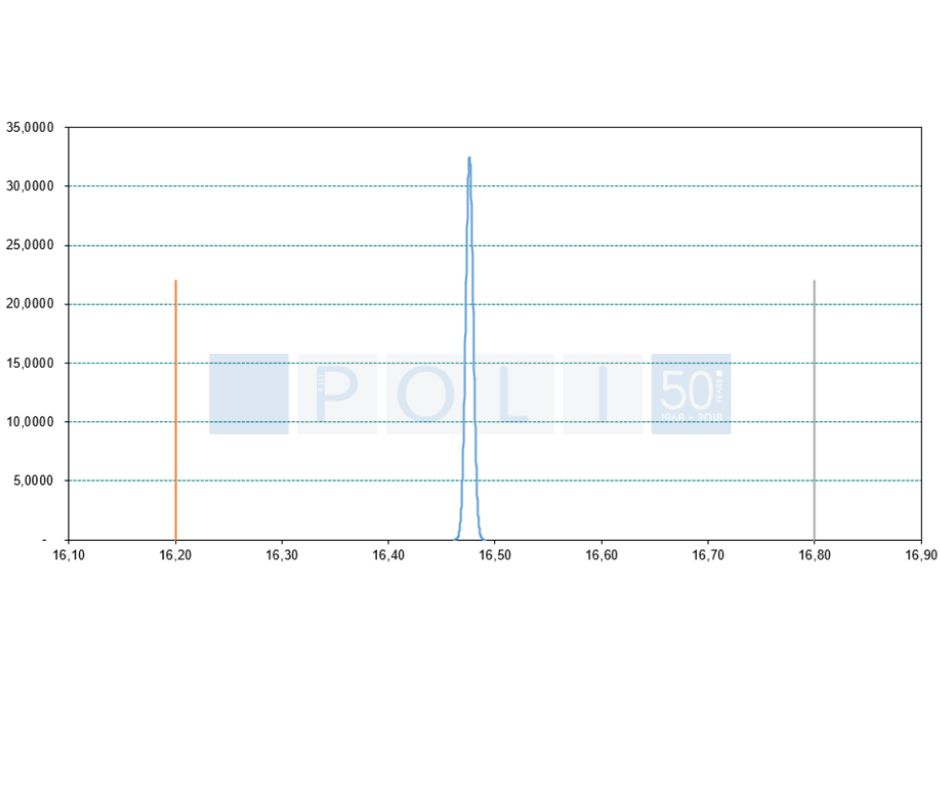
In the automotive industry, the process capability indices Cp Cpk are very common for the part dimensional inspection. This method compares the client’s specification given with the tolerance range (Voice of Customer) with the variability of the production quality of the process (Voice of Process).
In the case of a stable process such as cold metal stamping, following indices are used:

Cp is the ratio of the width of the tolerance range accepted by the client (Voice of customer) to 6 times the standard deviation σ of the values obtained from the mean (Voice of process).
The higher the Cp-value, the more stable the process is (σ small i.e. low variance). A very high Cp indicates a very high and narrow (Gaussian) distribution of the measured value. The Cpk, on the other hand, also introduces the mean value of the measurements taken.

This fact means that Cpk indicates in some way where the process places the mean value of the measured quantity in relation to the tolerance limits.
In the picture, you can see the ideal condition: the process is very stable (very high bell curve and therefore high Cp) with the position of the curve centred compared to the tolerance limits (position of the bell curve centred with respect to the tolerance limits).
8. PRODUCTION
F.lli Poli can provide the customer with a mass production service too.
Those who have experience with dies for metal stamping (but a similar argument also applies to plastic moulding) know there is a problem that should not be underestimated: the possible conflict of responsibility in the attribution of moulding problems.
When the company running the part production is not the die manufacturer and stamping problems occur there is often a rebound of responsibility between the die user (according to him the problem is caused by the design and type of die) and the die manufacturer (who blames the die user for the problem).
Any problems arising during stamping (production errors requiring unscheduled maintenance) become another moment of tension between the parties: who will pay for such extraordinary maintenance?
For this reason, it is certainly a great advantage to rely on companies, like F.lli Poli, that are able to act as a single supplier and sole responsible for the entire production process: from die manufacture to mass production.