Manufacturing of metal components for Refrigeration (HVAC)
The Refrigeration Sector (or, more precisely, HVAC – Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) is a sector that considerably requires metalworking skills.
Thanks to its extensive experience in this sector, F.lli Poli has been providing companies in the market with valuable manufacturing, and research and development support.
The main component with which we have gained a great deal of experience is the core of the process: the device performing the heat exchange.
Such device is designed to transfer heat between two bodies, more specifically between two fluids even if in different states, whilst keeping them separate (to avoid contamination) by means of a surface made of suitable material.
These can be divided into:
- Heat Exchangers
These heat a stream of fluid and, at the same time, refrigerate another one; fluids do not undergo a phase change and service fluids are not used. - Heaters or Coolers
These do not differ substantially from exchangers; their only purpose is to heat or cool a stream using service fluids, regardless of what happens to them - Condensers and evaporators
In these devices, phase transitions take place. In condensers, one of the fluids condenses releasing condensation heat; in evaporators, one of the fluids vaporizes as a result of the heat provided by another fluid. - Reboilers
The heat for the vaporisation of the fluid is not released by another fluid, but rather by radiation (flames)
A further classification is based on the morphology of the product. In particular, the following devices are available:
- Tube-type
- Plate-type
Plate heat exchange devices (whether or not deep-drawn) are indeed what we, at Fratelli Poli, are proudly and highly experienced with.
Materials
For heat exchange devices, it is crucial to identify the type of application in order to choose the most suitable material.
Two parameters shall mainly be considered (in addition to the specific parameters of heat exchange engineering itself)
The first one is the corrosive aggressiveness of the fluids; the second one is the operating temperature of the device (and, in particular, of the exchange surface).
These two parameters area correlated: as the operating temperature increases, it can trigger corrosive conditions which would otherwise be tolerated at lower temperatures.
Therefore, for HVAC, stainless steel is the most commonly used material.
In particular cases, aluminium might also be an option, but its chemical resistance is not as high, and its use shall be limited to relatively low temperature environments.
In particularly chemically aggressive applications, titanium is certainly advantageous thanks to its features, but it makes welding harder, and it is only used in particular applications due to its cost.
As for as stainless steel is concerned, particular attention shall be paid to reboiler applications. In this case, temperatures around stainless steel can be very high (direct flame contact).
For such applications, it must be ensured that neither fuel nor comburent release aggressive compounds such as chlorides and fluorides when the exchange surface is in contact with flames.
Inconel and Nimonic are particularly suitable materials for these applications.
Manufacturing Technologies
A typical application in the HVAC field is the forming of plates, which are then welded to create the exchange assembly.
- DRAWING DIES
Plates manufacturing is basically performed by constructing drawing dies.
It is not deep-drawing, but rather drawing creating multiple cavities which are then used in exchangers to create the turbulence needed to optimise the heat exchange between the fluid and the plate.
Technically, although not deep, such drawing is not insignificant, as it is all over the surface. During forming, it will be necessary to move the material correctly towards the drawing points to avoid any dangerous thin areas.
Titanium poses some forming constraints in terms of drawing depth. In the titanium forming process, it is necessary to activate sliding planes when drawing reaches certain depths (depending on the starting diameter). Such sliding planes are activated by heating at controlled temperatures.
- WELDING
After forming, the next stage is welding; this will result in groups of plates suitably assembled in order to allow the exchange medium to flow.
Welding around the perimeter can be performed (normally using Tig Technology to ensure tightness) while spot welding will be used if plates need to be secured to some internal points, which is often necessary.
As we develop dies, we provide our expertise to weigh the pros and cons before deciding whether to make progressive drawing dies or compound dies.
We assist our clients in determining the most suitable solution, so that they can, in turn, provide the end customer with a high-quality service.
HOW WE CREATE VALUE
When developing products for HVAC, our extensive experience enables us to provide solutions after assessing several options.
Normally, Simulations are not needed for this type of product, but a high level of planarity is essential.
Our special technologies allow us to measure planarity on complex surfaces.
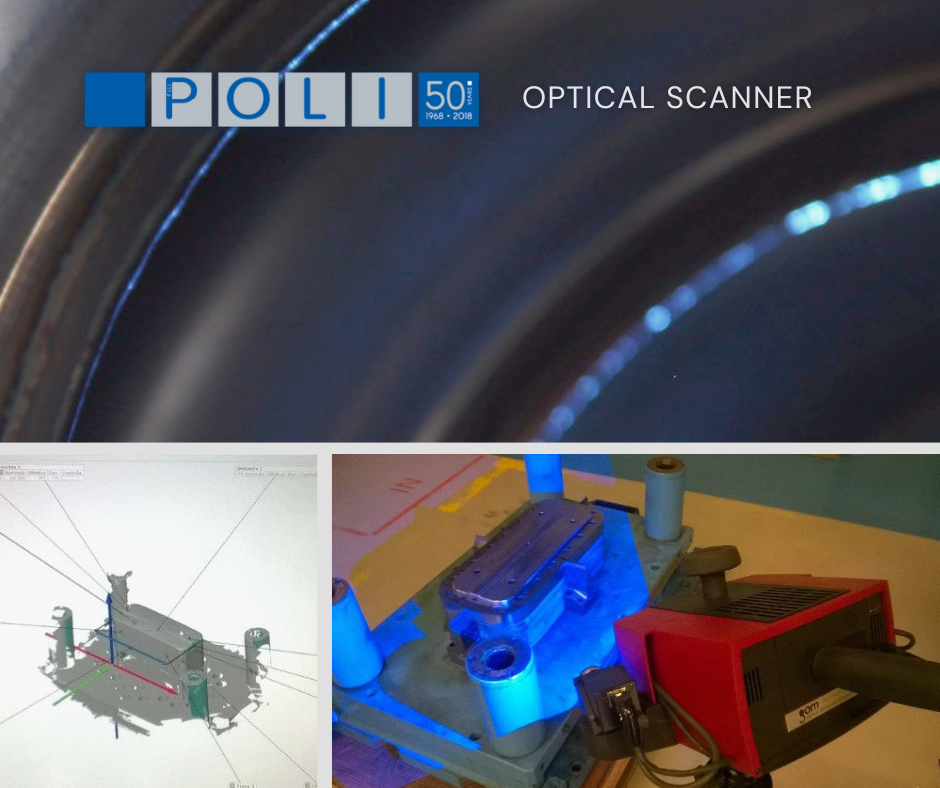
OPTICAL SCANNER
Our latest generation scanner is extremely effective, allowing us to assess whether a piece is congruent with the product we have received the 3D geometry for.
This system also enables us to measure the thickness at all the most critical points (which, for deep-drawing, are those where major stretching has occurred).
3D LASER
At F.lli Poli, we boast a 3D Laser which allows us to minimise equipment development costs, as we simply do not need to develop a trimming die. In this case, the client can delay investing in a trimming die until the number of ordered pieces is over a certain amount (with an investment payback period of two years or less).
This type of service is preferred by those clients who, for any reason, cannot clearly forecast how many items the market is ready to absorb.
F.lli Poli’s offer gives them the opportunity to start with minimal investment costs and then increase them when yearly product numbers to be manufactured exceed a specific amount.
We help our client monitor and calculate what threshold manufacturing level triggers the development of trimming dies.
Our dies and forming proposals are based on these technologies, which allow us to provide a constant level of very high quality of supply.
Not only do we provide our clients with dies and part production, but also with a support service to help them identify the most performing material, therefore we are able to meet the most complex demands and the highest quality expectations of our clients.